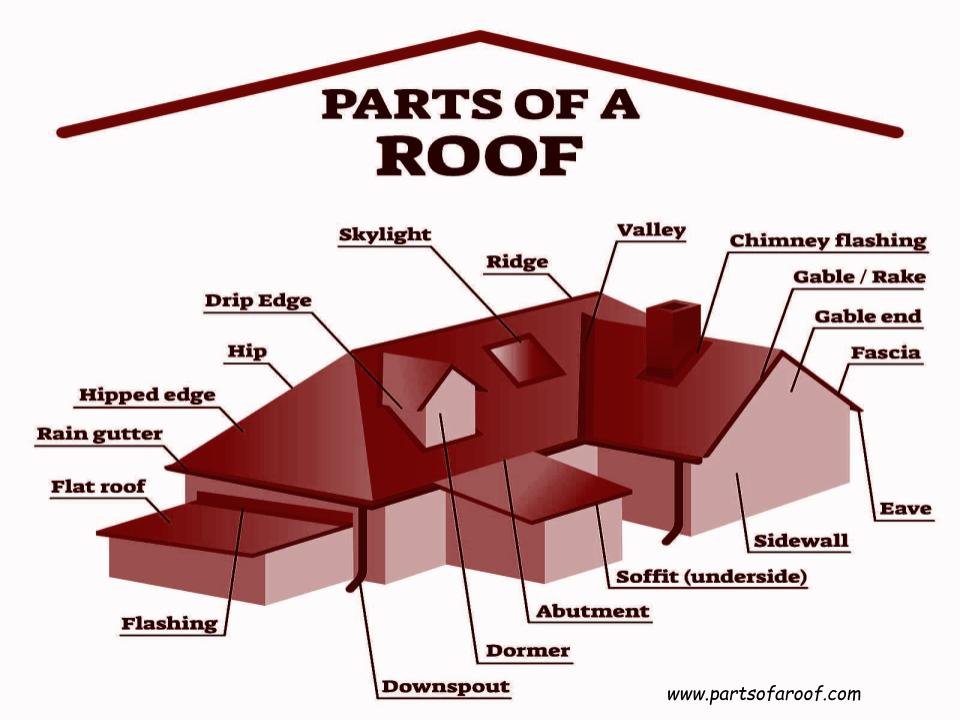
Whether you are a homeowner, roofing company employee, or aspiring contractor it is important to know the most common roof components and what they do. Below you will find the American Commercial Roofing, Inc. Asphalt Shingle Vocabulary List. This list doesn’t feature every component one might find on an asphalt roof, but it does cover all the main parts of an asphalt roof system.
If you want more information about any particular roof component, click the corresponding links to dive deeper into their design, functions, cost, and/or how they may show up in an insurance claim situation. If there are any you need more information on or a product that is missing you would like to learn more about – leave a comment or call us at (800)674-9535.
1. Asphalt Shingles
- Location: Cover the entire roof surface.
- Function: Serve as the primary waterproof layer, protecting the roof from rain, wind, and UV rays.
- Composition: Typically made of a fiberglass mat saturated with asphalt, topped with mineral granules for UV protection and aesthetic appeal.
2. Roof Decking (Sheathing)
- Location: Directly beneath the roofing materials, covering the rafters.
- Function: Provides a stable surface to which the shingles and other roofing materials are attached. It also supports the weight of the roofing materials and any snow or debris.
- Composition: Usually made of plywood or oriented strand board (OSB).
3. Roof Underlayment
- Location: Installed directly on top of the roof decking, under the shingles.
- Function: Acts as a secondary moisture barrier, protecting the roof deck from water infiltration.
- Composition: Traditionally made of asphalt-saturated felt paper (15 or 30 pounds), but newer synthetic underlayments are also common.
4. Drip Edge
- Location: Installed along the edges of the roof, including eaves and rakes.
- Function: Directs water away from the fascia and prevents water from seeping under the shingles. Also provides support for shingles at the roof’s edge.
- Composition: Made of metal, usually aluminum or galvanized steel.
5. Fascia
- Location: Runs along the lower edge of the roof, covering the ends of the rafters.
- Function: Provides a finished edge for the roof and supports the lower edge of the roof shingles. It also helps to protect the roof edge from weather.
- Composition: Typically made from wood, but can also be made from PVC or composite materials.
6. Soffit
- Location: The underside of the roof’s overhang (eaves).
- Function: Provides ventilation to the attic and roof deck, helping to regulate temperature and moisture levels. It also protects the rafters from the elements.
- Composition: Made from vinyl, aluminum, or wood.
7. Ridge Cap Shingles
- Location: Installed at the peak (ridge) of the roof.
- Function: Protects the roof’s ridge from water penetration and adds a finished look to the roof’s apex.
- Composition: Usually made from the same materials as the shingles, but are specially designed to conform to the ridge of the roof.
8. Ridge Vent
- Location: Installed along the peak of the roof under the ridge cap shingles.
- Function: Allows hot, moist air to escape from the attic, promoting ventilation and preventing heat and moisture buildup, which can damage the roof and reduce energy efficiency.
- Composition: Made of molded plastic or metal with a design that allows airflow while keeping out rain and pests.
9. Starter Strip Shingles
- Location: Installed at the eaves and rakes before the first row of shingles.
- Function: Provides a secure and straight base for the first row of shingles, helping to prevent wind uplift.
- Composition: Asphalt starter strips are similar to asphalt shingles, but are a single piece of asphalt with a sealant strip at the edge of the shingle to help seal eave shingles against wind uplift.
10. Valley Flashing
- Location: Installed in the roof valleys where two roof planes meet.
- Function: Directs water flow off the roof and prevents water from penetrating the roof valley, which is a vulnerable area.
- Composition: Usually made of metal, such as aluminum, copper, or galvanized steel.
11. Ice and Water Shield
- Location: Installed under the shingles at roof edges, valleys, and around penetrations.
- Function: Provides an additional layer of protection against ice dams and water infiltration, especially in areas prone to heavy rain or snow.
- Composition: A self-adhesive membrane made from rubberized asphalt, which seals around nails and prevents water from penetrating.
12. Roof Vents
- Location: Installed in various locations on the roof, including ridge, soffit, and gable areas.
- Function: Facilitates the proper airflow in the attic, helping to regulate temperature and moisture, which prolongs the roof’s lifespan and improves energy efficiency.
- Types: Ridge vents, box vents, turbine vents, and powered attic vents.
13. Flashing
- Location: Installed around roof penetrations, such as chimneys, skylights, and vents, as well as in roof valleys.
- Function: Seals joints and seams to prevent water infiltration.
- Composition: Typically made of metal, such as aluminum, copper, or galvanized steel.
14. Gutters and Downspouts
- Location: Attached to the roof edges along the eaves.
- Function: Collects and directs rainwater away from the roof and foundation to prevent water damage.
- Composition: Made from materials like aluminum, vinyl, steel, or copper.
15. Hip and Ridge
- Location: Hip shingles are installed on the roof’s hip (the angle where two roof slopes meet), while ridge shingles are installed along the roof’s peak.
- Function: Protects these critical roof areas from water penetration and provides a finished look.
- Composition: Made from the same materials as the asphalt shingles but are specially designed to fit these angles.
16. Roof Jacks
- Location: Around pipes or vents that penetrate through the roof.
- Function: Seals the area around the penetration to prevent water infiltration.
- Composition: Usually made of metal or rubber.
17. Pipe Boots
- Location: Around plumbing vents on the roof.
- Function: Seals the area around the vent pipes to prevent water infiltration.
- Composition: Usually made of rubber or flexible plastic, with a metal base.
18. Chimney Flashing
- Location: Installed around the chimney where it meets the roof.
- Function: Prevents water from seeping into the chimney structure and roof deck.
- Composition: Typically made of metal, such as galvanized steel, aluminum, or copper.
19. Chimney Cap
- Location: Installed on top of the chimney.
- Function: Prevents rain, snow, debris, and animals from entering the chimney, while allowing smoke and gases to escape. It also helps to prevent downdrafts and moisture damage to the chimney.
- Composition: Typically made of metal, such as stainless steel, copper, or galvanized steel.